What are varicose veins?
A varicose vein (varix) is a swollen and twisted blood vessel that can be seen just under the skin’s surface. The veins visibly bulge and usually appear in the legs. Weakened valves and veins can increase the blood pressure in a person’s legs, which can cause varicose veins. In the United States, nearly 23% of adults have the condition, which doctors rarely associate with health risks. Varicose veins are sometimes called “spider veins.” While varicose veins on their own are not dangerous, they can lead to further complications with you combine varicose veins and blood clots.
What is a blood clot?
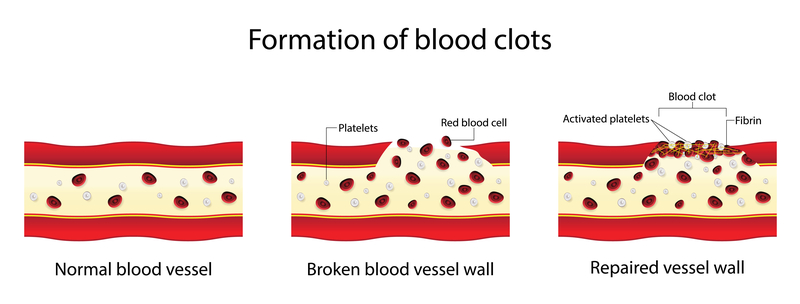
A blood clot is a lump of blood that has started to coagulate or thicken. Clots are made up of cells called platelets and connective tissue fibers (known as fibrin). Clots act as plugs in the body’s circulatory system to prevent excessive bleeding after an injury or from a breach in a vessel.
When blood clots form in response to an injury, they are beneficial as they stop further bleeding. However, some blood clots can be dangerous because they form without good reason and don’t dissolve on their own.
As clots form in the body, they can block the flow of oxygen-rich blood through vessels, possibly leading to damaged tissues.
A blood clot that forms in the circulatory system and inhibits blood flow is called a thrombus. These blood clots inside your veins may require medical attention, especially if found in your legs, lungs, or brain. If not treated promptly with anticoagulants (blood thinners) or corrective surgery, severe blood clots can be deadly.
Are varicose veins a warning sign of potentially deadly blood clots?
Varicose veins, usually caused by circulation issues, pregnancy, or the effects of age weakening the blood vessels, are common. They can make your legs swell, ache and feel heavy.
Are varicose veins a sign that blood clots are forming in the body? The short answer is yes. Varicose veins are one of the many warning signs of dangerous varicose vein symptoms like blood clots which can claim lives if they go undetected for too long.
Can varicose veins increase your risk of developing deep vein thrombosis (DVT)?
While most varicose veins run close to the skin and typically cause discomfort rather than danger, it’s natural to wonder if they can pave the way for more serious problems like deep vein thrombosis (DVT). DVT refers to a blood clot that forms in the deeper veins, most often in the legs, and can be life-threatening if it travels to the lungs.
Superficial veins (the ones affected by varicose veins) are generally less likely to create clots that move into the lungs. However, if your varicose veins become more pronounced or severe, your risk of developing DVT may rise. In rare cases, clots might form in deeper veins beneath the surface—these are the clots that can become a medical emergency.
If you have especially large, painful, or worsening varicose veins, it’s important to discuss your situation with your healthcare provider. They can help determine your personal DVT risk and recommend any monitoring or preventive steps, especially if you have other risk factors such as limited mobility, a history of blood clots, or major surgery.
Paying attention to any sudden changes in your legs—like significant swelling, redness, or persistent pain—should prompt a call to your doctor.
Why are varicose veins a sign of blood clots forming
Varicose veins are a sign of possible blood clots forming because varicose veins develop when valves in the veins leading out from your legs fail to operate properly. This causes the blood to pool and swell the affected vein, causing varicose veins to form. When your blood pools together from circulation issues, the platelets are more likely to start sticking together, forming a clot. Seeing a varicose vein on the outside is a sign that clots may be forming deeper on the inside.
How do you know if you have blood clots?
The most common symptoms that indicate you have a blood clot include:
- Being unable to move parts of your body due to pain, especially if other symptoms do not accompany this pain.
- An intense burning sensation over an area(s) of your body.
- Excessive sweating over one or more areas of your body.
- A warm feeling that develops suddenly in an area of your body.
- Feeling lightheaded or faint intense itching.
Types of blood clots
A blood clot is a plug or mass formed in the blood. Blood clots can occur inside your arteries, veins, and lungs, as well as on the surface of organs.
The most common types are:
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): This type of clot occurs when a thrombus forms within a vein deep in the body, usually in the legs, but it can also occur in the arms or pelvis. Symptoms include leg swelling, pain and tenderness, and red/bluish discoloration of the skin. This clot may develop into an embolus which travels through the bloodstream to other parts of the body. If it becomes lodged, it may hinder blood flow to organs like the heart and lungs. When a deep clot travels to the lungs, it becomes a pulmonary embolus, which can be fatal.
- Superficial Blood Clots or Phlebitis: These types of clots occur just under the skin in varicose veins and damage blood vessels. They are common after an injury or surgery. These blood clots are not usually serious and generally do not travel deeper into the vascular system. Symptoms include leg pain, itching, or burning sensation. The skin may also appear swollen or varicose in the affected area.
- Pulmonary Embolisms (PE): These types of clots form in the legs but travel to the lungs via the bloodstream, where they lodge and prevent proper circulation to organs like the heart and lungs. This type includes blockages caused by deep vein thrombosis. PE is life-threatening if not treated immediately with anticoagulant medications such as Warfarin.
Facts about blood clots:
- Deep vein blood clots can dislodge and travel to the lungs. This is called pulmonary embolism.
- There are more deaths from pulmonary embolism than breast cancer, AIDS, and car accidents combined.
- Deep calf or thigh pain and swelling of the leg are signs of deep vein thrombosis.
- Blood clots also arise in varicose veins. This is called superficial phlebitis.
- Superficial phlebitis usually feels like a hard, tender lump on your lug.
- Blood clots can be very serious. Those that occur in varicose veins are usually smaller and less dangerous, but they still need to be treated by your doctor.
- If you have varicose veins and experience calf pain or swelling, it is vital to see a doctor promptly.
The risk factors for developing these types of clots
Anyone can develop varicose veins or a blood clot if they create an environment likely to cause vein inflammation. It is important to identify the factors that can increase your chances of developing varicose veins and/or a blood clot.
Key risk factors for varicose veins:
- Obesity (being overweight). Obesity puts extra pressure on varicose vein-prone areas of the body, such as the legs, which increases the likelihood of these problems developing varicose vein symptoms.
- Certain occupations. Occupations requiring prolonged standing are at higher risk because they require more weight bearing down on the thighs and legs. Certain professions with long commutes also fall into this category. Occupations like truck driving and pilots are varicose vein-prone occupations.
- Professional athletes. Contact sports players, such as football and basketball players, are at higher risk for varicose veins because of the combination of standing around a lot (which increases pressure) and constant physical activity, which causes forceful contraction of muscles, particularly in the legs. This can increase stress on veins.
- Age. With age comes increased exposure to gravity over time. Gravity pulls blood downward towards areas with less gravitational pull, like the feet, increasing varicose vein symptoms. Vein walls can also weaken with age.
Key risk factors for blood clots:
- Having varicose veins, varicose leg sores, and varicose ulcers. Blood clots form when a blood vessel is damaged or weakened. By having varicose veins, you are at an increased risk of developing blood clots because the vein walls no longer provide support to the vessels, and this increases the likelihood that they will break open.
- Slow blood flow, or stasis. Blood clots can be caused by poor circulation caused by varicose veins, prolonged periods of immobility, and major surgery.
- Abnormalities of blood clotting factors. A defect in blood clotting factors can lead to the formation of blood clots. Factors include: varicose veins, varicose leg sores, and varicose ulcers; prolonged periods of immobility; pregnancy and menopause (this includes oral contraceptives); anticoagulant medications such as aspirin or Warfarin; use of birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy; estrogen supplements after menopause; obesity; smoking cigarettes; a family history of blood clots (especially if your mother had varicose legs or varicosities); cancer, especially cancers that have spread to the bone marrow.
It’s crucial to be aware of symptoms of blood clots in the legs. This way, medical attention can be obtained and a diagnosis made. If you think you may have a blood clot, seek immediate medical attention. Contact The Vein Center today if you are looking for varicose vein removal options, varicose vein surgery, or are concerned about deep vein thrombosis. Our vein specialists know how to create a personalized treatment plan to treat your leg pain and make you feel and look your best.



